


At a symposium organized by the Moon Village Association, scientists presented ideas on establishing a human colony in the challenging lunar environment.



Japan's scientific and technological capabilities have declined since that inspiring experience. It's not too late to build again on what the Hayabusa achieved.
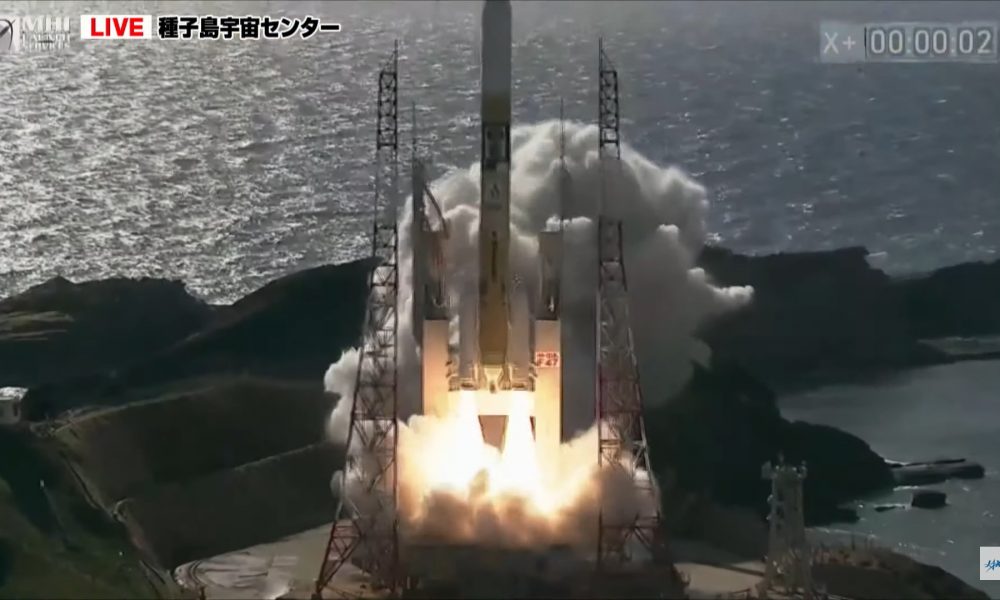



With the succesful launch of its SLIM lunar lander, Japan could become the fifth country to achieve a lunar landing, and it carried two different payloads.
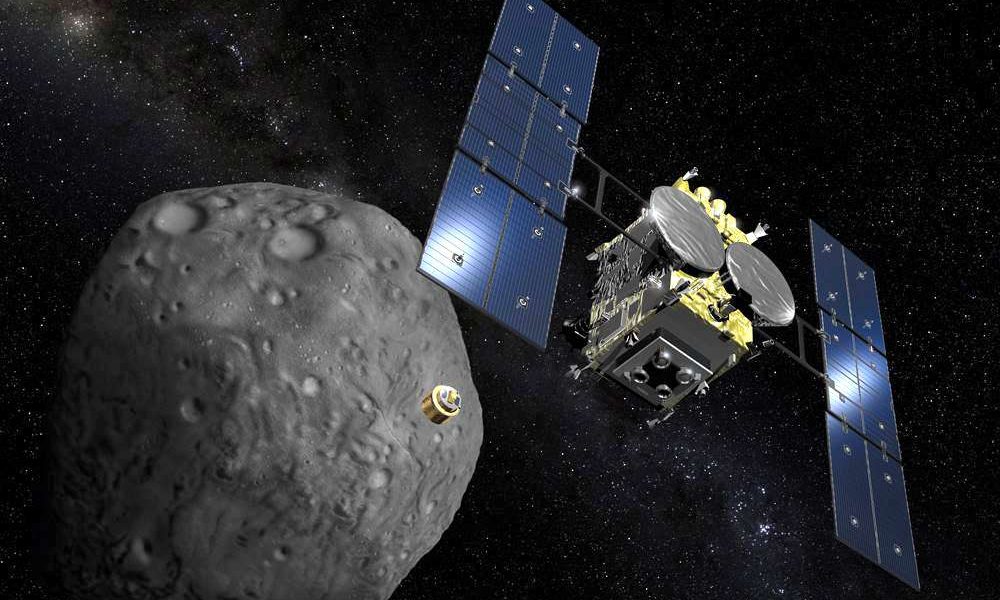



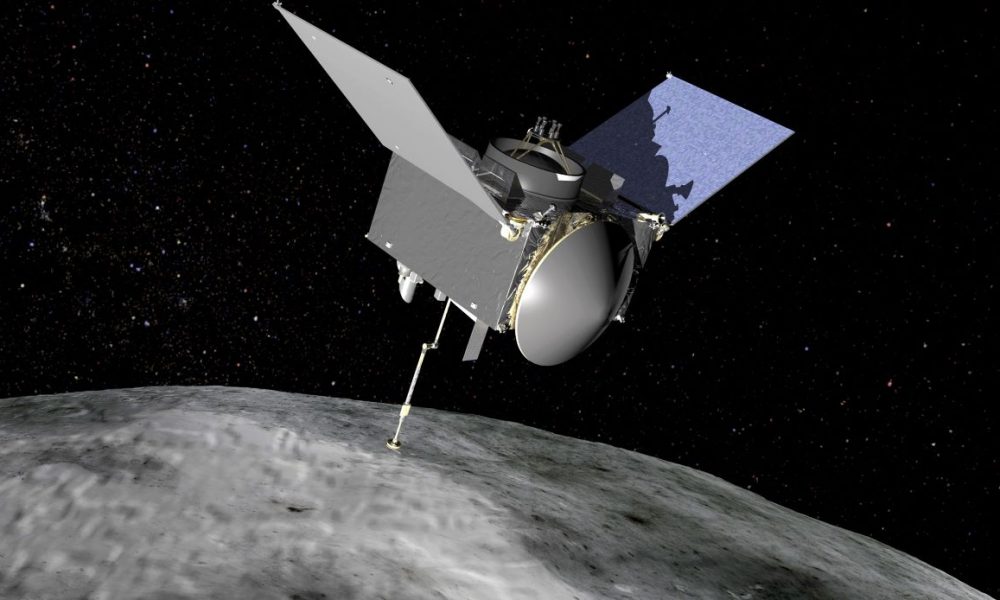
Samples collected from asteroid Ryugu by Hayabusa2 contain RNA base uracil and remnants of liquid water — shedding light on the origins of life.
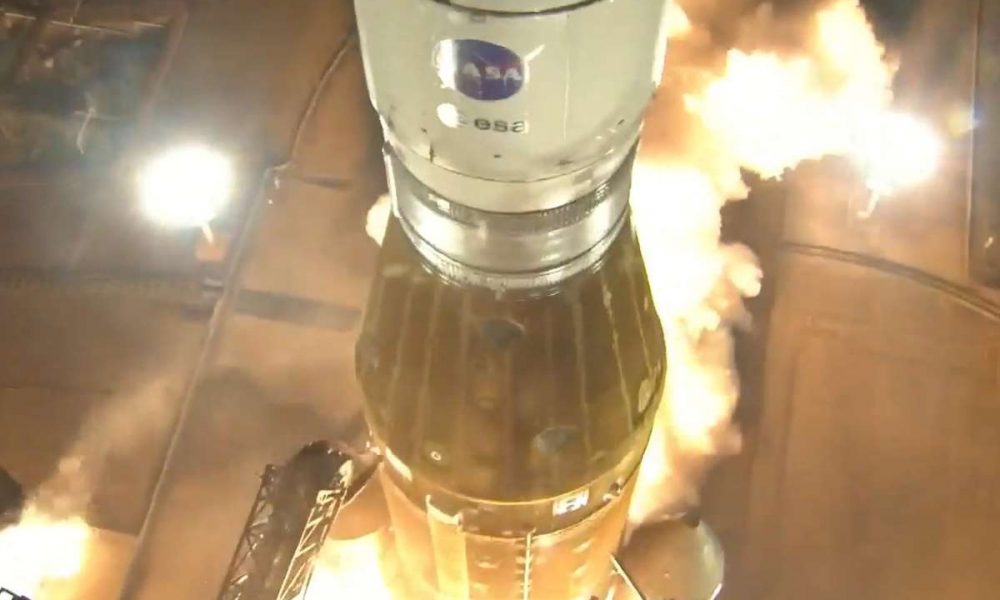



OMOTENASHI failed, but the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency has a history of turning initial failures into ultimate successes. Remember the Hayabusa2.
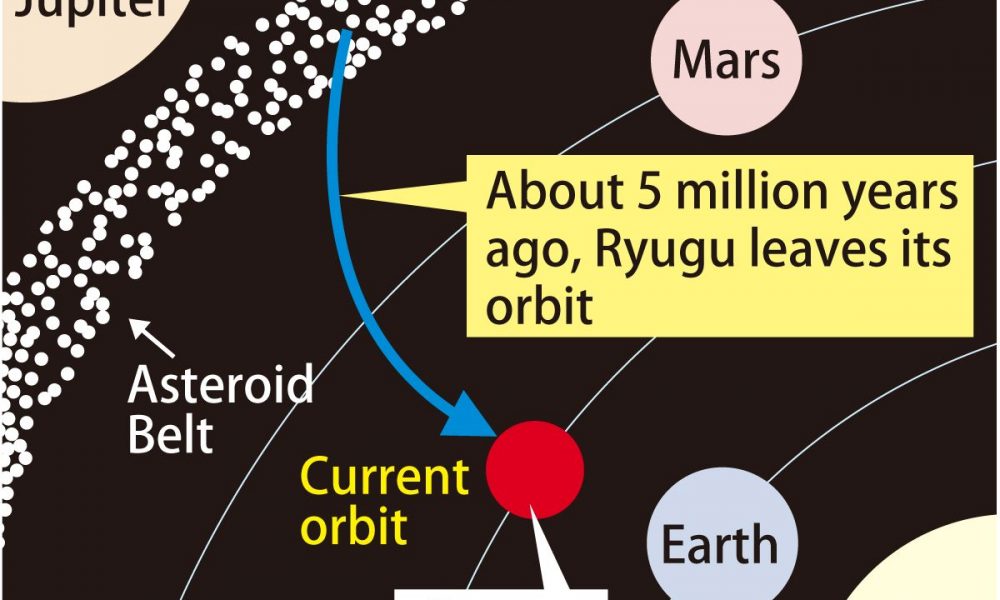
Samples from Ryugu sent back to earth by Hayabusa2 have led to startling discoveries about the power of cosmic rays and the makeup of asteroids.
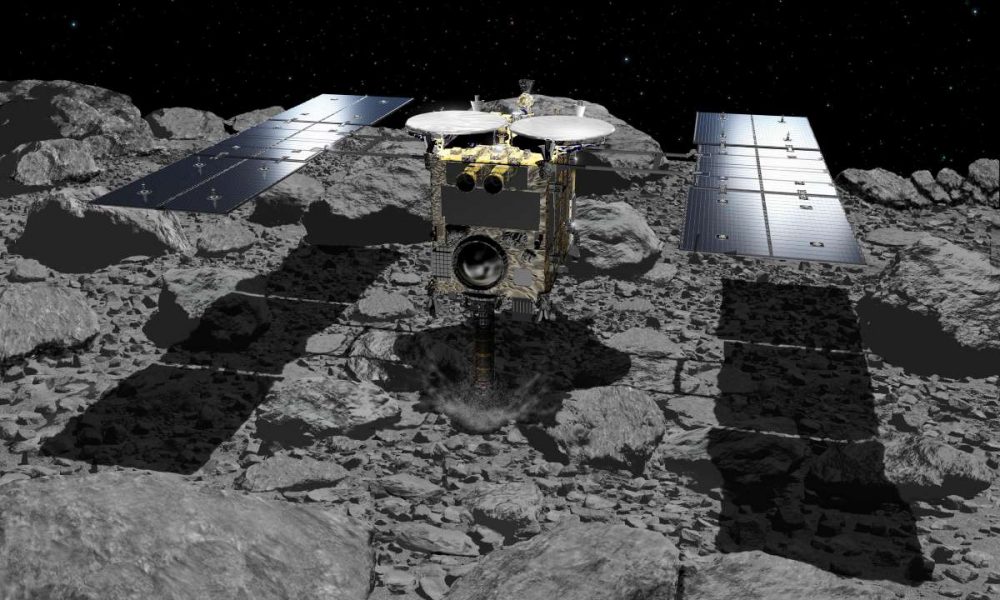



Research institutes around the world analyzing the asteroid’s sand samples have found more than 20 kinds of amino acids, the building blocks of life.
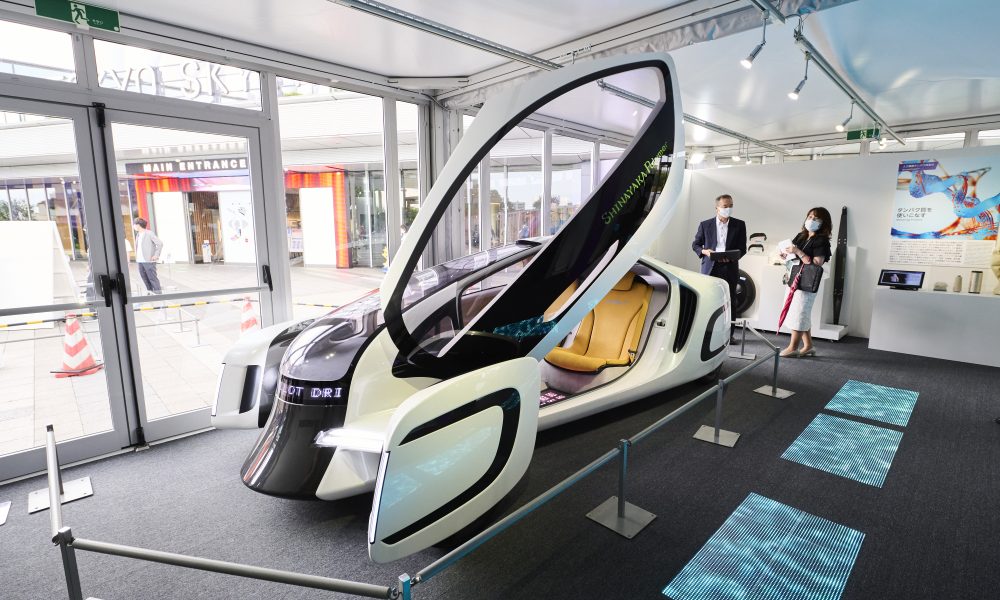



From the deep sea to outer space, “This exhibit will act as a catalyst for people to imagine a little bit about what Society 5.0 will...
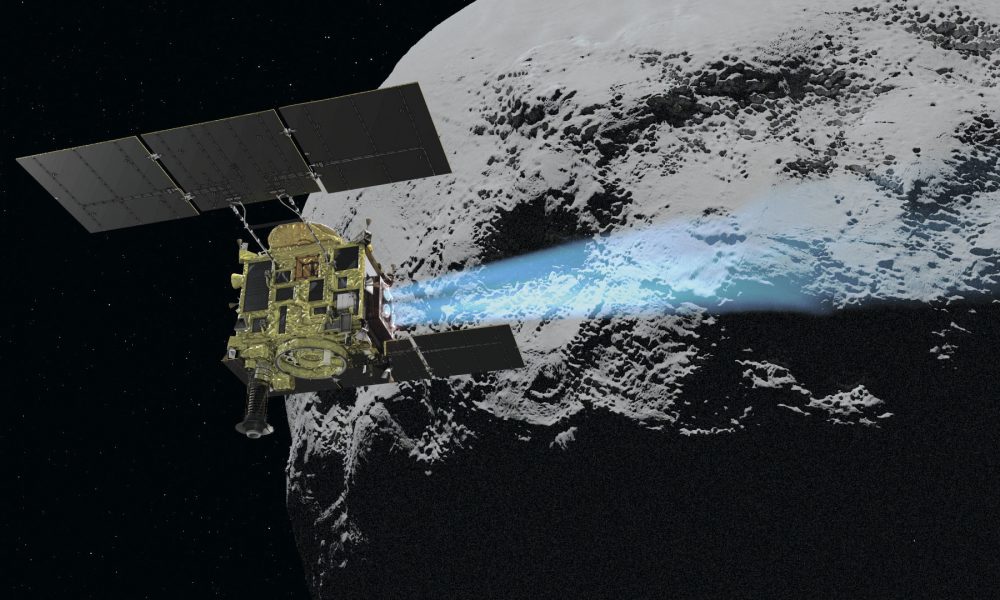



Hayabusa2 became the first spacecraft in the world to successfully collect samples from the subsurface of Ryugu in 2019, sending 5.4 grams of rocks and sand...



For Tokyo University, the main objective is to use the technology developed for local problem solving. But the team is also aiming to contribute to JAXA’s...



As Japan races to meet its net zero carbon emissions, a Japanese company is helping to pave the way with batteries that meet the challenge for...
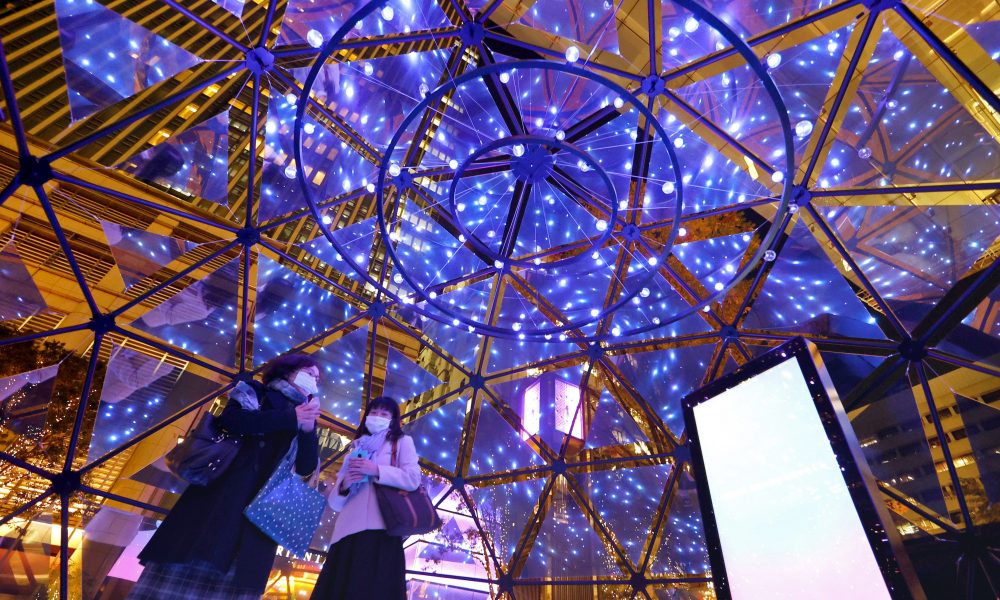



Japan makes up for its short history celebrating the Christmas holiday with an abundance of creativity and array of winter illuminations